Your vehicle's oxygen (O2) sensor is a small but mighty component, acting as a crucial monitor for your emissions system. It constantly measures oxygen levels in the exhaust, sending vital data to the engine's computer. This information allows the computer to maintain the perfect air-to-fuel ratio, ensuring optimal performance, better fuel economy, and lower emissions.
When this sensor begins to fail, it can trigger a cascade of issues, from a noticeable drop in gas mileage to the risk of severe engine or catalytic converter damage. Many drivers mistake these bad O2 sensor symptoms for more complex mechanical failures, leading to unnecessary stress and costly, incorrect repairs. This guide is designed to prevent that.
We will break down the seven most common signs of a failing oxygen sensor. You'll learn how to identify each symptom, understand its impact on your vehicle, and know exactly what steps to take next. Recognizing these warnings early is key to protecting your vehicle's long-term health and your budget, ensuring you know precisely when it's time to bring your car to the ASE-certified professionals at Kwik Kar Oil Change and Auto Care for an accurate diagnosis.
1. Check Engine Light (CEL) Illumination
The most common and immediate indicator of a problem with your vehicle's emissions system is the illumination of the check engine light (CEL) on your dashboard. This warning light is your car's primary way of telling you that the engine control unit (ECU), the onboard computer, has detected a fault. A failing oxygen sensor is one of the most frequent triggers for the CEL, making this one of the key bad o2 sensor symptoms to watch for.

When an O2 sensor begins to fail, it sends erratic or incorrect data about the oxygen levels in the exhaust to the ECU. The computer interprets this faulty data as a problem with the air-fuel mixture or the catalytic converter's efficiency, logging a specific Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and activating the warning light to alert you.
Why You Can't Ignore the CEL
Ignoring the check engine light is a gamble that can lead to more significant and costly problems. A faulty O2 sensor can cause a cascade of issues, from poor fuel economy and reduced engine performance to catastrophic damage to your catalytic converter, a repair that can cost thousands.
Key Insight: The check engine light doesn't just signal a current problem; it’s a preventative warning. Addressing it promptly by diagnosing the underlying code can save you from far more expensive repairs and ensure your vehicle passes its next emissions inspection.
For Richardson-area drivers and fleet managers, seeing this light is a clear signal to seek professional diagnostics. For instance, a daily commuter might notice the light turn on during their drive on US-75, or a fleet manager might spot it during a routine vehicle check. Both scenarios demand the same immediate action: a professional code reading to pinpoint the exact cause. While the CEL can indicate various issues, understanding what the check engine light means is the first step toward a correct diagnosis.
Actionable Steps for Drivers
If your check engine light comes on, don't panic. Unless the light is flashing (which indicates a severe misfire requiring you to pull over immediately), you can typically drive to a trusted service center.
- Schedule a Diagnostic Test: Contact an ASE-certified facility like Kwik Kar right away to have the OBD-II codes read. This is the only way to confirm if a bad O2 sensor is the culprit.
- Note the Conditions: Pay attention to how your car is driving. Is there a loss of power? Are you getting worse gas mileage? Make a note of when the light appeared and any other symptoms you’ve noticed.
- Don't Disconnect the Battery: Resetting the light by disconnecting the battery erases the stored fault codes, making it much harder for a technician to diagnose the root problem.
2. Poor Fuel Economy and Increased Consumption
One of the most financially impactful bad o2 sensor symptoms is a sudden and noticeable drop in your vehicle's fuel economy. The oxygen sensor plays a direct role in managing the engine's air-to-fuel ratio. When it fails, it can no longer provide accurate oxygen readings from the exhaust, often leading the engine control unit (ECU) to default to a "rich" fuel mixture, meaning it injects more fuel than necessary as a protective measure. This inefficiency directly translates to more frequent trips to the gas station.
This decline in efficiency can be significant, with a faulty O2 sensor potentially reducing your miles per gallon (MPG) by up to 40%. For Richardson families watching their budget or small business fleet managers overseeing operational costs, this increase in fuel consumption becomes a serious financial drain. What might start as a minor annoyance can quickly escalate into a substantial, ongoing expense.
Why Your MPG Is a Critical Diagnostic Clue
Tracking your vehicle's fuel consumption is more than just good financial practice; it’s a proactive way to monitor engine health. A sudden, unexplained decrease in MPG is often one of the first and only outward signs of a failing sensor before more severe symptoms appear. A daily commuter might notice their car that usually gets 250 miles per tank is now struggling to reach 150 miles. This is a clear red flag.
Key Insight: A sharp drop in fuel economy is your engine's way of telling you it's running inefficiently. A bad O2 sensor forces the engine to guess the proper fuel mixture, and it almost always guesses wrong by adding too much fuel, wasting money and increasing emissions.
Addressing this symptom promptly not only restores your vehicle's efficiency but also prevents the long-term damage that a rich fuel mixture can cause. Excess fuel can wash oil from cylinder walls and foul spark plugs, leading to more complex and expensive engine repairs down the road. Ignoring the drop in MPG is like ignoring a leak in your wallet.
Actionable Steps for Drivers
If you suspect your fuel economy is suffering due to a sensor issue, here are some practical steps to take:
- Track Your MPG: Start manually calculating your miles per gallon on each fill-up. Record your mileage and the amount of gas you add, then divide the miles driven by the gallons used. This gives you concrete data to share with a technician.
- Schedule a Diagnostic Check: A drop in fuel economy can have multiple causes. The only way to confirm if a bad O2 sensor is the culprit is to have a professional technician, like the ASE-certified team at Kwik Kar, run a computerized diagnostic test.
- Rule Out Other Factors: Consider if other variables have changed. Have your driving habits become more aggressive? Are your tires properly inflated? Eliminating these simple factors helps isolate the problem.
3. Rough Idle and Engine Hesitation
One of the most noticeable and concerning bad o2 sensor symptoms is a sudden change in your engine's smoothness. When a sensor provides incorrect data to the engine control unit (ECU), it disrupts the delicate air-fuel balance required for stable combustion. This leads to a rough, shaky idle where the RPM needle may jump erratically, and the vehicle vibrates more than usual while stopped. You might also feel a distinct hesitation or stumble when you try to accelerate.
A faulty O2 sensor can cause the ECU to command an overly rich (too much fuel) or lean (too little fuel) mixture at the wrong times. This inconsistent combustion process is what you feel as a rough idle or hesitation. The engine is essentially struggling to run efficiently because it's not receiving the correct amount of fuel for the given conditions.
Why You Can't Ignore Engine Instability
For anyone who relies on their vehicle for critical work, like first responders, military personnel, or on-call healthcare workers, a hesitant engine is more than an annoyance; it’s a reliability issue. For instance, a first responder can't afford a vehicle that stumbles when responding to an emergency call. A healthcare worker needs to know their car will start and drive smoothly when paged for an urgent situation. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to engine stalling, reduced power, and unpredictable performance, creating potential safety hazards.
Key Insight: Rough idling and hesitation are direct feedback from your engine that something is wrong with its core combustion process. While other issues can cause this, a failing O2 sensor is a primary suspect because it directly controls the air-fuel mixture, and prompt diagnosis is crucial to restore vehicle reliability and prevent stalling.
It's important to distinguish the cause, as a rough idle can also point to other problems. A comprehensive guide on bad spark plug symptoms can help you understand related issues, but professional diagnostics are the only way to be certain.
Actionable Steps for Drivers
If your engine starts running rough or hesitating, taking systematic steps can help a technician diagnose it faster.
- Note the Conditions: Pay attention to when the issue occurs. Does it happen on a cold start, after the engine is warm, or only when you accelerate? This context is vital for diagnosis.
- Record Any Other Signs: Listen for unusual sounds like popping or sputtering from the exhaust and feel for any new vibrations. The more information you can provide, the better.
- Schedule Diagnostics Immediately: Don't wait for the problem to worsen. A rough idle puts extra strain on engine and transmission mounts and can precede a complete stall. Contact Kwik Kar for an expert diagnostic check.
4. Black Smoke or Excessive Emissions from Exhaust
One of the most visually alarming bad o2 sensor symptoms is the appearance of black smoke billowing from your exhaust pipe. This isn't just a cosmetic issue; it's a direct sign of a severe fuel-air mixture imbalance inside your engine. When an O2 sensor fails, it often defaults to sending a "lean" signal to the ECU, tricking the computer into thinking there's too much oxygen in the exhaust. The ECU's response is to overcompensate by injecting an excessive amount of fuel into the cylinders.
This rich fuel mixture cannot burn completely during the combustion cycle. The unburned fuel particles are then expelled through the exhaust system, manifesting as thick, sooty black smoke. You might also notice a strong smell of gasoline when the car is running and a buildup of black residue on your tailpipe. For Richardson drivers, this is a critical issue that directly impacts vehicle emissions and the ability to pass a state inspection.
Why Excessive Emissions Are a Red Flag
Ignoring black exhaust smoke is a recipe for costly engine and emissions system damage. The constant rich condition not only wastes a significant amount of fuel but also washes protective oil from cylinder walls, accelerating engine wear. More critically, the unburned fuel travels downstream and can overheat and destroy the catalytic converter, a component that can cost thousands of dollars to replace.
Key Insight: Black smoke is your car’s way of showing you it’s running too rich. This symptom is a clear indicator that a critical sensor, often the O2 sensor, has failed and is causing your vehicle to pollute excessively and risk severe component damage. Prompt diagnosis is essential to prevent a minor sensor issue from becoming a major repair bill.
A local commuter in Richardson might notice a puff of black smoke in their rearview mirror when accelerating onto the President George Bush Turnpike, or a fleet manager could fail a vehicle during an internal emissions check. Both scenarios point to an urgent need for professional diagnostics to avoid a failed state inspection and ensure the vehicle is operating efficiently and cleanly.
Actionable Steps for Drivers
If you see black smoke coming from your exhaust, it’s a sign that your vehicle requires immediate attention.
- Schedule a Diagnostic Service: Contact a reputable auto care center like Kwik Kar immediately. A technician can perform a comprehensive emissions system analysis and read the OBD-II codes to confirm if a faulty O2 sensor is the cause.
- Document the Symptoms: Note when the smoke appears. Is it constant, only during startup, or just when you accelerate hard? This information helps the technician diagnose the problem more efficiently.
- Check Your Tailpipe: Look for a dry, black, sooty residue on the tip of the exhaust pipe. This is physical evidence that confirms the engine is running too rich.
5. Catalytic Converter Degradation and Damage
One of the most severe and costly consequences of ignoring other bad o2 sensor symptoms is the eventual failure of your catalytic converter. This critical emissions component relies on precise data from the O2 sensors to function correctly. A failing sensor that causes the engine to run consistently rich will send unburned fuel into the exhaust system, effectively poisoning and overheating the converter.
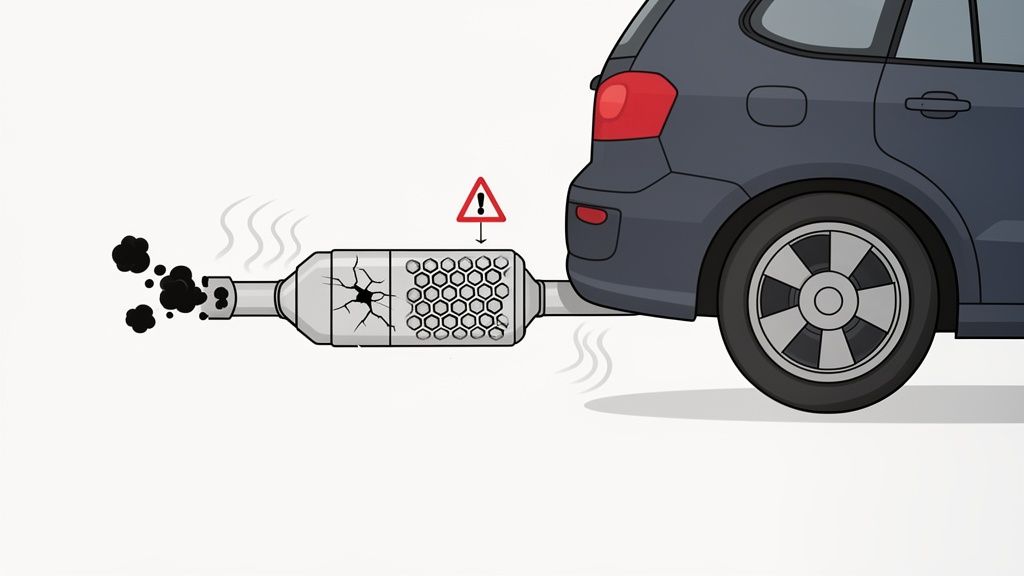
This raw fuel superheats the delicate internal ceramic honeycomb, melting and destroying the precious metals that convert harmful pollutants into less dangerous gases. Over time, this leads to a complete blockage or failure of the converter, a repair that can easily cost between $800 and $2,500, depending on the vehicle.
Why You Can't Ignore the Risk
A failed catalytic converter is not just an expensive repair; it's a major system failure that will prevent your vehicle from passing an emissions test and can cause significant backpressure, leading to severe engine damage. For owners of aging or high-mileage vehicles, this can be a financially crippling repair that was entirely preventable.
Key Insight: Viewing O2 sensor replacement as preventative maintenance is a cost-effective strategy. Spending a relatively small amount to replace a failing sensor proactively can save you from the multi-thousand-dollar expense of a catalytic converter replacement down the road.
For a fleet manager in Richardson, neglecting a single faulty O2 sensor could cascade into multiple vehicles needing new converters, drastically increasing operational costs. Similarly, a family with an older vehicle could face an unexpected and budget-breaking repair bill. Early diagnostics at the first sign of trouble, like a check engine light or poor fuel economy, is the best defense against this expensive outcome.
Actionable Steps for Drivers
Proactive measures are key to protecting your catalytic converter from damage caused by a bad O2 sensor.
- Act Immediately on Other Symptoms: If you notice poor fuel economy, a rough idle, or a check engine light, schedule a diagnostic scan immediately. Don't wait for the problem to worsen.
- Request Specific Code Checks: When you bring your vehicle in for service, ask the technician to check for codes related to catalytic converter efficiency (like P0420 or P0430) alongside O2 sensor codes.
- Schedule Preventative Replacement: On vehicles approaching or exceeding 100,000 miles, consider replacing the upstream O2 sensors as a preventative measure to ensure the air-fuel ratio remains accurate and protects the converter.
6. Failed Emissions Inspection and Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Perhaps the most definitive sign of a sensor issue is failing a state-mandated emissions inspection. This failure is almost always tied to specific Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in your vehicle's computer. A faulty oxygen sensor is a primary culprit for emissions-related failures, making this one of the most conclusive bad o2 sensor symptoms you can encounter.
When an O2 sensor malfunctions, it can no longer accurately monitor and help regulate the emissions control system. The Engine Control Unit (ECU) detects this failure and logs specific codes, such as P0131 (O2 Sensor Low Voltage) or P0133 (O2 Sensor Slow Response). These codes will cause an automatic failure during an OBD-II emissions test, a required part of vehicle registration in the Richardson area.
Why You Can't Ignore Emissions Failures
A failed emissions test isn't just an inconvenience; it has legal and financial consequences. In Texas, you cannot renew your vehicle's registration without passing this inspection, leading to potential fines and the inability to legally drive your car. This can be a major disruption for anyone, from a daily commuter to a healthcare worker who depends on their vehicle for work.
Key Insight: A failed emissions test is your vehicle's final warning that an underlying problem needs immediate attention. The specific DTCs provide a direct roadmap for technicians, pointing straight to the failing component, which is often an O2 sensor that has been degrading over time.
For Richardson-area drivers, this scenario is all too common. A fleet manager might see P0133 codes flagged during an annual compliance check, grounding multiple vehicles. A local commuter might be surprised by a P0131 code during their routine state inspection, preventing them from renewing their registration. Both situations demand a professional diagnosis and repair to get back on the road legally.
Actionable Steps for Drivers
If your vehicle fails its emissions inspection due to O2 sensor-related codes, you have a clear path to resolution.
- Get a Professional Scan: Bring your vehicle to an ASE-certified shop for a comprehensive diagnostic test. Technicians can confirm the codes and perform further tests to pinpoint the exact sensor that has failed. You can learn more about professional engine diagnostics to understand the process.
- Request the Code Report: Ask for a printout of all DTCs and any associated freeze frame data. This information is crucial for an accurate repair and serves as a valuable part of your vehicle's service history.
- Address and Re-Test: Once the faulty O2 sensor is replaced, the technician will clear the codes. You can then return for an emissions re-test to complete your vehicle's registration.
7. Engine Knock, Pinging, and Detonation
A less common but highly damaging sign of a sensor problem is the sound of engine knock, also known as pinging or detonation. This metallic rattling or pounding sound, often more noticeable during acceleration, indicates that the air-fuel mixture is igniting improperly in the cylinders. A failing oxygen sensor can directly contribute to this dangerous condition, making it a critical one of the bad o2 sensor symptoms to recognize.
When an O2 sensor fails, it can cause the engine to run either too rich or, more commonly in this case, too lean. An excessively lean mixture (too much air, not enough fuel) increases the temperature inside the combustion chamber. This heat can cause the fuel to ignite prematurely before the spark plug fires, creating a shockwave that you hear as a distinct "knock" or "ping."
Why You Can't Ignore Engine Knock
Persistent engine knocking is not just an annoying noise; it's the sound of your engine slowly destroying itself. The uncontrolled explosions place extreme stress on critical internal components like pistons, connecting rods, and crankshaft bearings. Left unaddressed, this can lead to catastrophic engine failure, a repair far more severe and costly than replacing an O2 sensor.
Key Insight: Engine knock is a direct warning of abnormal combustion. While a bad O2 sensor is a potential cause, this symptom demands immediate professional diagnosis to prevent irreversible internal engine damage.
For owners of aging or high-mileage vehicles in the Richardson area, hearing a new knock during their morning commute down Campbell Road is a serious cause for concern. Similarly, a fleet manager responsible for high-use vehicles must address reports of engine pinging immediately to protect the longevity of their assets. Ignoring it can quickly turn a minor sensor issue into a major engine overhaul.
Actionable Steps for Drivers
If you hear a knocking or pinging sound from your engine, you should treat it as a serious issue that requires prompt attention.
- Reduce Engine Load: Immediately ease off the accelerator. Knocking is often most severe under heavy load, so driving gently can help minimize damage as you head to a repair shop.
- Note When it Happens: Pay close attention to the conditions. Does the knock occur during acceleration, at a steady highway speed, or when the engine is cold? This information is vital for an accurate diagnosis.
- Schedule Immediate Diagnostics: Contact an ASE-certified facility like Kwik Kar without delay. Technicians can use advanced diagnostic tools to determine if the knock is caused by a lean condition from a bad O2 sensor or other issues like carbon buildup or a faulty knock sensor.
Bad O2 Sensor: 7-Symptom Comparison
| Issue | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases / Tips | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Check Engine Light (CEL) Illumination | Low → automatic detection; diagnosis needs OBD-II scan | OBD-II scanner (professional recommended); short shop visit | Identifies fault codes early; enables targeted repair and prevents escalation | All drivers — get immediate diagnostic at a certified shop; note when light first appeared | High effectiveness for early detection and proactive maintenance ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Poor Fuel Economy and Increased Consumption | Medium → requires data collection and differential diagnosis | Track MPG over multiple fill-ups; diagnostic scan; possible O2 sensor replacement | MPG can improve 10–40% after repair; reduces operating cost | Budget-conscious drivers and fleets — log fuel use consistently; verify pre/post repair | Direct measurable cost savings; clear financial motivation to repair ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Rough Idle and Engine Hesitation | Medium → may require broader ignition/fuel-system checks | OBD-II scan, inspection of spark/plugs/injectors; technician time | Restores smooth idle and responsiveness; reduces stall risk | Safety-critical drivers — schedule prompt diagnostics and record conditions | Immediate drivability improvement; safety benefit ⭐⭐ |
| Black Smoke / Excessive Exhaust Emissions | Low detection, Medium diagnosis → visible symptom but needs emissions testing | Visual documentation, emissions test, possible sensor or catalytic repair | Eliminates visible smoke; reduces pollution; improves chance to pass inspection | Emissions-sensitive owners — photograph symptoms; seek urgent repair to avoid fines | Highly visible sign prompting fast action; supports regulatory compliance ⭐⭐ |
| Catalytic Converter Degradation and Damage | High → secondary damage with complex replacement | Comprehensive diagnostics; catalytic converter replacement (costly, time‑consuming) | Prevents or repairs major converter failure; avoids long‑term engine issues | High‑mileage and fleet owners — prioritize preventive O2 sensor replacement | Major cost avoidance when detected early; prevents catastrophic failure ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Failed Emissions Inspection and Diagnostic Trouble Codes | Low → codes are definitive; Medium if wiring/multiple faults present | Professional OBD-II scan, code interpretation, emissions re-test | Resolves codes and restores registration eligibility; documents freeze‑frame data | All owners in regulated areas — obtain printout, fix promptly, re-test | Clear diagnostic pathway to compliance and legal relief ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Engine Knock, Pinging, and Detonation | Medium–High → multiple possible causes require thorough analysis | In‑depth diagnostics (knock sensors, fuel trim, timing); possible engine repairs | Prevents internal engine damage; resolves abnormal combustion | Owners of aging/high‑mileage vehicles — stop driving if knock occurs; diagnose urgently | Protects engine longevity; prevents costly internal repairs ⭐⭐ |
Your Next Steps for a Healthy Engine
Navigating the various bad O2 sensor symptoms we've detailed, from a persistent check engine light to a sudden drop in fuel efficiency, can feel overwhelming. You’ve learned that a failing oxygen sensor is more than a minor annoyance; it’s a critical component failure that directly impacts your engine's performance, your wallet at the gas pump, and the environment. Ignoring these warning signs, such as a rough idle or black exhaust smoke, is a gamble that can lead to far more severe and expensive consequences, including irreversible damage to your catalytic converter.
The most important takeaway is that these symptoms are your vehicle's way of communicating a problem that requires prompt and accurate diagnosis. While a simple OBD-II scanner can point you in the right direction, it doesn’t tell the whole story. The codes triggered by a bad O2 sensor can sometimes mimic other issues, making professional diagnostics essential for an effective and cost-efficient repair. Taking decisive action not only restores your vehicle's power and fuel economy but also ensures you can pass your next emissions inspection with ease.
Turning Knowledge into Action
Understanding the problem is the first step, but what comes next is crucial. If you're experiencing several of these issues, particularly engine hesitation or audible knocking, it's best to limit your driving. In severe cases where engine performance is drastically compromised, leaving the car immobile and stranded is a real possibility. In these situations, having a reliable contact for immediate help is invaluable; professional 24/7 roadside assistance services can safely transport your vehicle to a repair shop without risking further damage.
For most drivers, the immediate next step is clear:
- Don't ignore the Check Engine Light: It’s your primary warning.
- Schedule a professional diagnostic scan: This is the only way to confirm if the O2 sensor is the true culprit.
- Address the issue promptly: Delaying the repair will only cost you more in fuel and potential collateral damage to other expensive components.
By proactively addressing these symptoms, you are not just fixing a small part; you are preserving the overall health and longevity of your engine. You are investing in reliable transportation for your family, ensuring your work vehicle stays on the road, and protecting your budget from the shock of a catastrophic, multi-thousand-dollar repair bill. A healthy engine is a safe and dependable engine, and it all starts with listening to what it's trying to tell you.
Don't let a faulty sensor dictate your vehicle's health and your peace of mind. The ASE-certified technicians at Kwik Kar Oil Change and Auto Care have the expertise and diagnostic tools to accurately identify and resolve any O2 sensor-related issues. Schedule your diagnostic appointment with us today and drive with the confidence that comes from expert care.